lv mv and hv voltage ranges | extra high voltage range lv mv and hv voltage ranges What is the definition of Low Voltage, Medium Voltage and High Voltage? Electrical power systems can be divided into three main categories: generation, transmission and distribution. Because efficiency considerations each of these . Situs Resmi LOUIS VUITTON Indonesia - Temukan koleksi terbaru Wanita koleksi Gelang, tersedia secara eksklusif di louisvuitton.com dan butik-butik Louis Vuitton
0 · what is high voltage hv
1 · what is ehv in electrical
2 · low medium high voltage ranges
3 · is 11kv low voltage
4 · hv meaning in electrical
5 · extra high voltage range
6 · difference between hv and lv
7 · classification of voltage levels
METEOFOR: Weather in Riga for 10 days, weather forecast for 10 days, Riga, Latvia. Riga 10-Day Weather Forecast. Tu. 14 May. We. 15. Th. 16. Fr. 17. Sa. .
Typically, the voltage level between the 220kV to 760 kV is called Extra High voltages. Example for 400 kV: Dehar – Panipat Line. Example for 760kV: .
burberry finsdale wool toggle coat reviews
What is the definition of Low Voltage, Medium Voltage and High Voltage? Electrical power systems can be divided into three main categories: generation, transmission and distribution. Because efficiency considerations each of these .High (HV), Extra- High (EHV) & Ultra-High Voltages (UHV) - 115,000 to 1,100,000 VAC. Medium Voltage (MV) - 2,400 to 69,000 VAC. Low Voltage (LV) - 240 to 600 VAC. Generac issued a .The basic structure of voltage classifications remains consistent across most standards, though there can be slight variations in voltage ranges depending on specific documents or standards. .
As electrical professionals, many of us have been coming across the terms LV or LT, MV, HV or HT & EHV or EHT in our day-to-day professional lives. But are we aware of the .High voltage or HV: 45 kV to 230 kV; Medium voltage or MV: 1000 V to 45 kV; Low voltage or LV: up to 1000V; EHV is generated at a high level to account for losses encountered between . Understanding voltage classification is essential for the proper application and safety of electrical systems. Voltage classifications typically include Low Voltage (LV), Medium .
“3.1 Low Voltage (LV): A class of nominal system voltages 1,000V or less. 3.2 Medium Voltage (MV): A class of nominal system voltages greater than 1,000V and less than .
High Voltage (HV): between 45 kV and 230 kV. Extra High Voltage (EHV): from 230 kV and above. As a general rule, LV cables might be used in applications like fixed wiring; MV cables .
Typically, the voltage level between the 220kV to 760 kV is called Extra High voltages. Example for 400 kV: Dehar – Panipat Line. Example for 760kV: Anpara – Unnao. Ultra-High voltage: The ultra-high voltage lines are nothing but a voltage level above 800kV is called Ultra-high voltage. Example: 1200kV Bina National
What is the definition of Low Voltage, Medium Voltage and High Voltage? Electrical power systems can be divided into three main categories: generation, transmission and distribution. Because efficiency considerations each of these categories are operated in .High (HV), Extra- High (EHV) & Ultra-High Voltages (UHV) - 115,000 to 1,100,000 VAC. Medium Voltage (MV) - 2,400 to 69,000 VAC. Low Voltage (LV) - 240 to 600 VAC. Generac issued a white paper titled Medium Voltage On-Site Generation Overview. The white paper compares NEC to ANSI Standards.The basic structure of voltage classifications remains consistent across most standards, though there can be slight variations in voltage ranges depending on specific documents or standards. The widely accepted classifications are as follows: Low Voltage (LV): ≤1 kV; Medium Voltage (MV): >1 kV to <100 kV; High Voltage (HV): 100 kV to <230 kV
Voltage Classes according to NSI C84.1-2016. LV = Low Voltage: <1000 V; MV = Medium Voltage: >1kV & <100 kV; HV = High Voltage: >100 kV & ≤ 230 kV; EHV = Extra-High Voltage: >230 kV but <1000 kV; UHV = Ultra-High Voltage: ≥1000 kV; Voltage Levels in the United States 120V. The standard voltage in the US is 120 volts – 60 Hz single phase . As electrical professionals, many of us have been coming across the terms LV or LT, MV, HV or HT & EHV or EHT in our day-to-day professional lives. But are we aware of the limits of these voltages as per Indian Standards and/or International Standards?
High voltage or HV: 45 kV to 230 kV; Medium voltage or MV: 1000 V to 45 kV; Low voltage or LV: up to 1000V; EHV is generated at a high level to account for losses encountered between generation and point of use. Low Voltage Classification. Low-voltage installations are standard in domestic and commercial premises, and the UK enforces the Low . Understanding voltage classification is essential for the proper application and safety of electrical systems. Voltage classifications typically include Low Voltage (LV), Medium Voltage (MV), and High Voltage (HV), each serving distinct purposes in power distribution and usage. “3.1 Low Voltage (LV): A class of nominal system voltages 1,000V or less. 3.2 Medium Voltage (MV): A class of nominal system voltages greater than 1,000V and less than 100kV. 3.3 High Voltage (HV): A class of nominal system voltages equal to or greater than 100kV and equal to or less than 230kV.High Voltage (HV): between 45 kV and 230 kV. Extra High Voltage (EHV): from 230 kV and above. As a general rule, LV cables might be used in applications like fixed wiring; MV cables are critical power distribution (both for local grid power and for heavy-duty equipment); HV cables are aerial cables - overhead line for widescale power .
Typically, the voltage level between the 220kV to 760 kV is called Extra High voltages. Example for 400 kV: Dehar – Panipat Line. Example for 760kV: Anpara – Unnao. Ultra-High voltage: The ultra-high voltage lines are nothing but a voltage level above 800kV is called Ultra-high voltage. Example: 1200kV Bina National
What is the definition of Low Voltage, Medium Voltage and High Voltage? Electrical power systems can be divided into three main categories: generation, transmission and distribution. Because efficiency considerations each of these categories are operated in .
what is high voltage hv
High (HV), Extra- High (EHV) & Ultra-High Voltages (UHV) - 115,000 to 1,100,000 VAC. Medium Voltage (MV) - 2,400 to 69,000 VAC. Low Voltage (LV) - 240 to 600 VAC. Generac issued a white paper titled Medium Voltage On-Site Generation Overview. The white paper compares NEC to ANSI Standards.The basic structure of voltage classifications remains consistent across most standards, though there can be slight variations in voltage ranges depending on specific documents or standards. The widely accepted classifications are as follows: Low Voltage (LV): ≤1 kV; Medium Voltage (MV): >1 kV to <100 kV; High Voltage (HV): 100 kV to <230 kVVoltage Classes according to NSI C84.1-2016. LV = Low Voltage: <1000 V; MV = Medium Voltage: >1kV & <100 kV; HV = High Voltage: >100 kV & ≤ 230 kV; EHV = Extra-High Voltage: >230 kV but <1000 kV; UHV = Ultra-High Voltage: ≥1000 kV; Voltage Levels in the United States 120V. The standard voltage in the US is 120 volts – 60 Hz single phase .
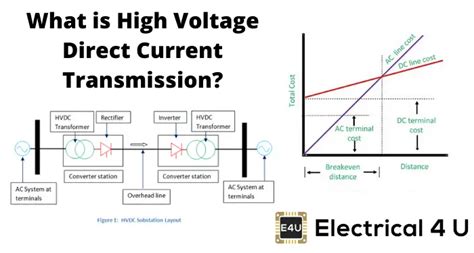
As electrical professionals, many of us have been coming across the terms LV or LT, MV, HV or HT & EHV or EHT in our day-to-day professional lives. But are we aware of the limits of these voltages as per Indian Standards and/or International Standards?High voltage or HV: 45 kV to 230 kV; Medium voltage or MV: 1000 V to 45 kV; Low voltage or LV: up to 1000V; EHV is generated at a high level to account for losses encountered between generation and point of use. Low Voltage Classification. Low-voltage installations are standard in domestic and commercial premises, and the UK enforces the Low . Understanding voltage classification is essential for the proper application and safety of electrical systems. Voltage classifications typically include Low Voltage (LV), Medium Voltage (MV), and High Voltage (HV), each serving distinct purposes in power distribution and usage. “3.1 Low Voltage (LV): A class of nominal system voltages 1,000V or less. 3.2 Medium Voltage (MV): A class of nominal system voltages greater than 1,000V and less than 100kV. 3.3 High Voltage (HV): A class of nominal system voltages equal to or greater than 100kV and equal to or less than 230kV.
what is ehv in electrical
Latvijas Ģeotelpiskās informācijas aģentūra (LĢIA) ir vadošā iestāde valsts politikas īstenošanā ģeodēzijas, kartogrāfijas un ģeotelpiskās informācijas jomā.
lv mv and hv voltage ranges|extra high voltage range